Chemistry Journal of Moldova
Ecological chemistry
Author(s):
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2023 Volume 18, no.2
Pages: 15-27
Vladyslav Zhezherya, Petro Linnik, Rostyslav Linnik
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2023 Volume 18, no.2
Pages: 15-27
Full Text (PDF): Download
https://doi.org/10.19261/cjm.2023.1091
Abstract (PDF)
Supplementary Material (PDF)
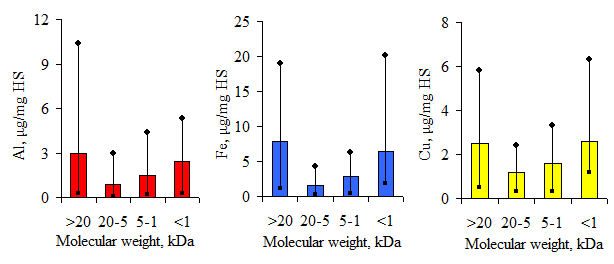
Graphical Abstract: The aim of this research work was to evaluate the role of different fractions of humic substances in the binding of Al(III), Fe(III) and Cu(II) ions into complexes. The share of humic substances with a molecular weight of 20–5 kDa increases from 37% to 59%, when the total concentration of humic substances also increases. It was established that humic substances with molecular weight 20–5 kDa bounded the smallest amount of Al(III), Fe(III) and Cu(II) into complexes.
Downloads: 46
Author(s):
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2023 Volume 18, no.2
Pages: 28-34
Muslim Hasan Allawi, Riyadh Sadeq ALMukhtar, Shurooq Talib Al-Humairi, Ali Dawood Salman, Tatjána Juzsakova, Viktor Sebestyén, Igor Cretescu
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2023 Volume 18, no.2
Pages: 28-34
Full Text (PDF): Download
https://doi.org/10.19261/cjm.2023.1019
Abstract (PDF)
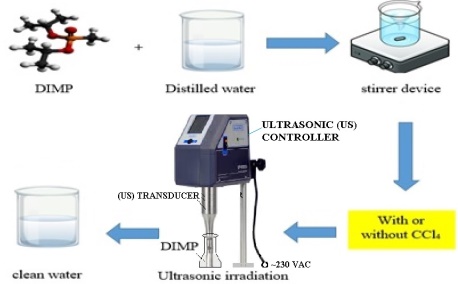
Graphical Abstract: The degradation of diisopropyl methylphosphonate (DIMP) in aqueous solutions was studied using ultrasound irradiation with a fixed frequency of 26.6 kHz, following the first-order kinetic model. The experimental parameters, including the pH, the initial concentration of DIMP, the processing time, and the concentration of the additive CCl4 were investigated. The best degradation efficiency of 98% was observed at pH of 10, adding 0.8 g/L CCl4 for a processing time of 45 min.
Downloads: 44
Author(s):
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2023 Volume 18, no.2
Pages: 35-44
Pavlo Kuzema, Iryna Laguta, Oksana Stavinskaya, Viktor Anishchenko, Anastasiia Kramar, Natalia Smirnova, Tetiana Fesenko, Roman Ivannikov, Oksana Linnik
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2023 Volume 18, no.2
Pages: 35-44
Full Text (PDF): Download
Abstract (PDF)
Graphical Abstract: The extracts from the leaves of Deschampsia antarctica, Camelina sativa, and Camellia japonica plants, as well as from Camelina sativa and Silybum marianum seedcakes were investigated as potential additives for improvement of biodiesel stability against oxidation. In spite of significant distinctions in the content of various phenolic compounds, all the extracts were found to effectively inhibit DPPH radicals and decelerate transformation of fatty acid esters of biodiesel into organic acids by ~9-26%. Various extracts were shown to have different activity towards the biodiesel from rape and camelina seed oils; this result is consistent with the assumption that there is no universal stabilizer for different types of biodiesel.
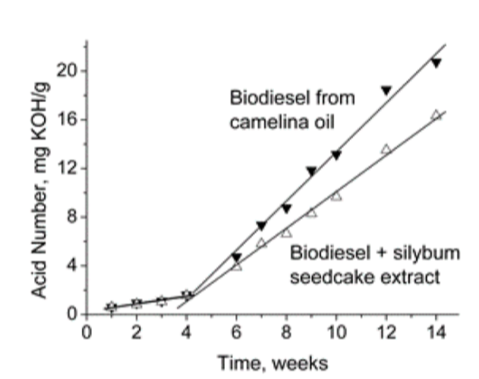
Graphical Abstract: The extracts from the leaves of Deschampsia antarctica, Camelina sativa, and Camellia japonica plants, as well as from Camelina sativa and Silybum marianum seedcakes were investigated as potential additives for improvement of biodiesel stability against oxidation. In spite of significant distinctions in the content of various phenolic compounds, all the extracts were found to effectively inhibit DPPH radicals and decelerate transformation of fatty acid esters of biodiesel into organic acids by ~9-26%. Various extracts were shown to have different activity towards the biodiesel from rape and camelina seed oils; this result is consistent with the assumption that there is no universal stabilizer for different types of biodiesel.

Downloads: 66
Author(s):
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2023 Volume 18, no.1
Pages: 46-51
Serghei Pogrebnoi, Nicolae Eremia, Dmitri Bilan, Lucian Lupascu, Natalia Bolocan, Gheorghe Duca, Svetlana Armasu, Dumitru Terteac, Vitalie Cebanu, Serghei Tincu, Alexandru Znagovan, Iulia Neicovcena, Olga Coseleva, Valerina Slanina, Fliur Macaev
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2023 Volume 18, no.1
Pages: 46-51
Full Text (PDF): Download
https://doi.org/10.19261/cjm.2023.924
Abstract (PDF)
Graphical Abstract: The chemical composition and antimicrobial activity of propolis ethanolic and water-ethanolic extracts from the central zone of Moldova have been investigated by GC-MS and liquid chromatography. There were found 21 amino acids, of which the most abundant were glutamic acid, alanine, leucine and isoleucine. The propolis extracts exhibited strong antioxidant (53.7 mg ascorbic acid eq./g extract or 113.4 mg Trolox eq./g extract and 87.5 mg ascorbic acid eq./g extract or 162 mg Trolox eq./g extract for ethanol, and water-ethanol extract, respectively) and antimicrobial activity (from 0.0055 up to 0.07%), suggesting their potential as natural agents for therapeutic use.
Graphical Abstract: The chemical composition and antimicrobial activity of propolis ethanolic and water-ethanolic extracts from the central zone of Moldova have been investigated by GC-MS and liquid chromatography. There were found 21 amino acids, of which the most abundant were glutamic acid, alanine, leucine and isoleucine. The propolis extracts exhibited strong antioxidant (53.7 mg ascorbic acid eq./g extract or 113.4 mg Trolox eq./g extract and 87.5 mg ascorbic acid eq./g extract or 162 mg Trolox eq./g extract for ethanol, and water-ethanol extract, respectively) and antimicrobial activity (from 0.0055 up to 0.07%), suggesting their potential as natural agents for therapeutic use.

Downloads: 130
Author(s):
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2023 Volume 18, no.1
Pages: 38-45
Maria Gonta, Gheorghe Duca, Elena Sirbu, Stefan Robu, Larisa Mocanu
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2023 Volume 18, no.1
Pages: 38-45
Full Text (PDF): Download
https://doi.org/10.19261/cjm.2023.910
Abstract (PDF)
Graphical Abstract: This paper presents the synthesis of a copolymer with reducing properties obtained by functionalizing chitosan with quercetin and determining the antioxidant activity of the derivatives obtained depending on the molar mass of the polymer. For this purpose, low molecular weight chitosan was obtained by oxidizing industrial chitosan with hydrogen peroxide and functionalizing with quercetin by the covalent grafting method. The comparative antioxidant properties of the composite obtained by grafting technical chitosan with quercetin and by grafting low molecular weight chitosan were studied by the DPPH (2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl radical) method. The obtained results indicate that a decrease in the molecular weight of chitosan contributed to its grafting with quercetin. As a result, the functionalized polymer composite acquired a higher antioxidant activity and can be successfully used to inhibit the oxidation of various organic substrates in the cosmetic, food and pharmaceutical industries.
Downloads: 91
Author(s):
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Review
Issue: 2023 Volume 18, no.1
Pages: 9-27
Petro Linnik, Vladislav Zhezherya, Rostyslav Linnik
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Review
Issue: 2023 Volume 18, no.1
Pages: 9-27
Full Text (PDF): Download
https://doi.org/10.19261/cjm.2023.1049
Abstract (PDF)
Graphical Abstract: The results of research on the metal mobility and the peculiarities of their migration in the "bottom sediments – water" system of surface water bodies are summarized. The distribution of metals between different fractions of the solid phase of bottom sediments affects the potential metal mobility and their migration in the "bottom sediments – water" system.
Graphical Abstract: The results of research on the metal mobility and the peculiarities of their migration in the "bottom sediments – water" system of surface water bodies are summarized. The distribution of metals between different fractions of the solid phase of bottom sediments affects the potential metal mobility and their migration in the "bottom sediments – water" system.
Downloads: 79
Author(s):
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2023 Volume 18, no.1
Pages: 28-37
Zainab Abdul-Zahra and Rashed Rasheed
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2023 Volume 18, no.1
Pages: 28-37
Full Text (PDF): Download
https://doi.org/10.19261/cjm.2023.1027
Abstract (PDF)
Graphical Abstract: This work is dedicated to the synthesis of ZnO and CeO2 nanopraticles with possible application for nitrite ions removal. The obtained nnaoparticles were characterized by X-ray diffraction, scanning electron microscopy, atomic force microscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy and UV-visible spectroscopy. Further, the produced nanoparticles were used to adsorb NO2- ions from aqueous solutions. The results showed that the nanoparticles which were heated at 90°C (hydroxide forms) presented a higher activity for nitrite ions removal than those that were heated at 400°C (oxide forms). This may be related to nitrite ions preferential adsorption to hydroxide forms rather than to oxide forms; in both cases (90°C and 400°C), zinc oxide nanoparticles presented higher nitrite removal activity.
Downloads: 66
Author(s):
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Invited paper
Issue: 2022 Volume 17, no.2
Pages: 7-18
Tudor Lupascu and Maria Sandu
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Invited paper
Issue: 2022 Volume 17, no.2
Pages: 7-18
Full Text (PDF): Download
Graphical Abstract: This paper presents the the main scientific and innovative results are presented, which were obtained by the talented chemist and renowned ecologist Valeriu Ropot throughout his scientific career. The results of scientific investigations are bestowed and analysed concerning the quality of the waters of the Dniester and the Prut Rivers, Dubasari reservoirs on the Dniester River, as well as the main bodies of water in the Republic of Moldova. The paper also includes the practical recommendations for reducing the negative impact on the environment, of the discharge of hundreds of thousands of tons of brine into the Dniester River as a result of the accident at the mineral fertilizer plant in the city of Stebnik, Ukraine. Moreover, the paper presents the results of studies aimed at developing methods for determining organic and inorganic pollutants in natural waters.
Downloads: 63
Author(s):
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2022 Volume 17, no.2
Pages: 35-42
Viacheslav Shvydkiy, Sergei Dolgov, Alexander Dubovik, Mikhail Kozlov, Alisa Povkh, Lyudmila Shishkina, Gheorghe Duca
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2022 Volume 17, no.2
Pages: 35-42
Full Text (PDF): Download
Abstract (PDF)
Graphical Abstract: This paper presents a study of the hydrochemical composition and physicochemical properties of natural water samples from various sources in the Voronezh and Moscow regions. Two model systems are proposed for assessing the state of the aquatic environment: UV spectroscopy with spectrum decomposition by the Gauss method and spontaneous aggregation of lecithin in a polar medium. Based on the performed investigation, it was determined that the size of lecithin aggregates decreases, and the value of their zeta potential increases with an increase in the content of hydrophobic compounds in natural water.
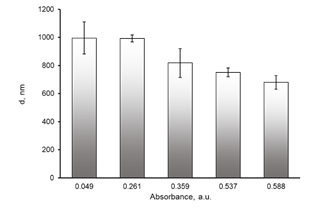
Graphical Abstract: This paper presents a study of the hydrochemical composition and physicochemical properties of natural water samples from various sources in the Voronezh and Moscow regions. Two model systems are proposed for assessing the state of the aquatic environment: UV spectroscopy with spectrum decomposition by the Gauss method and spontaneous aggregation of lecithin in a polar medium. Based on the performed investigation, it was determined that the size of lecithin aggregates decreases, and the value of their zeta potential increases with an increase in the content of hydrophobic compounds in natural water.
Downloads: 62
Author(s):
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2022 Volume 17, no.2
Pages: 43-49
Oksana Stavinskaya, Iryna Laguta, Pavlo Kuzema, Iryna Skorochod, Alla Roy, Ivan Kurdish
Field: Ecological chemistry
Type: Research paper
Issue: 2022 Volume 17, no.2
Pages: 43-49
Full Text (PDF): Download
Abstract (PDF)
Graphical Abstract: The work was aimed at preparing the CA+A300 composite consisting of caffeic acid (CA) and fumed silica (A300) and at comparing the properties of CA in the solution and in the composite. The results showed that the solution and the composite are effective antioxidant/antimicrobial agents and that inclusion of CA in the CA+A300 composite provides its gradual release into solutions and reaction mixtures, thus ensuring a prolonged action of the compound.
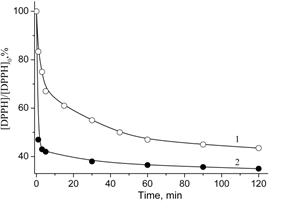
Graphical Abstract: The work was aimed at preparing the CA+A300 composite consisting of caffeic acid (CA) and fumed silica (A300) and at comparing the properties of CA in the solution and in the composite. The results showed that the solution and the composite are effective antioxidant/antimicrobial agents and that inclusion of CA in the CA+A300 composite provides its gradual release into solutions and reaction mixtures, thus ensuring a prolonged action of the compound.
Downloads: 73






